

5,6 Consequently, weight loss medications are a consideration as adjunctive therapy for diabetes prevention. 3,4 However, implementing lifestyle modification that results in sustainable weight loss is challenging.

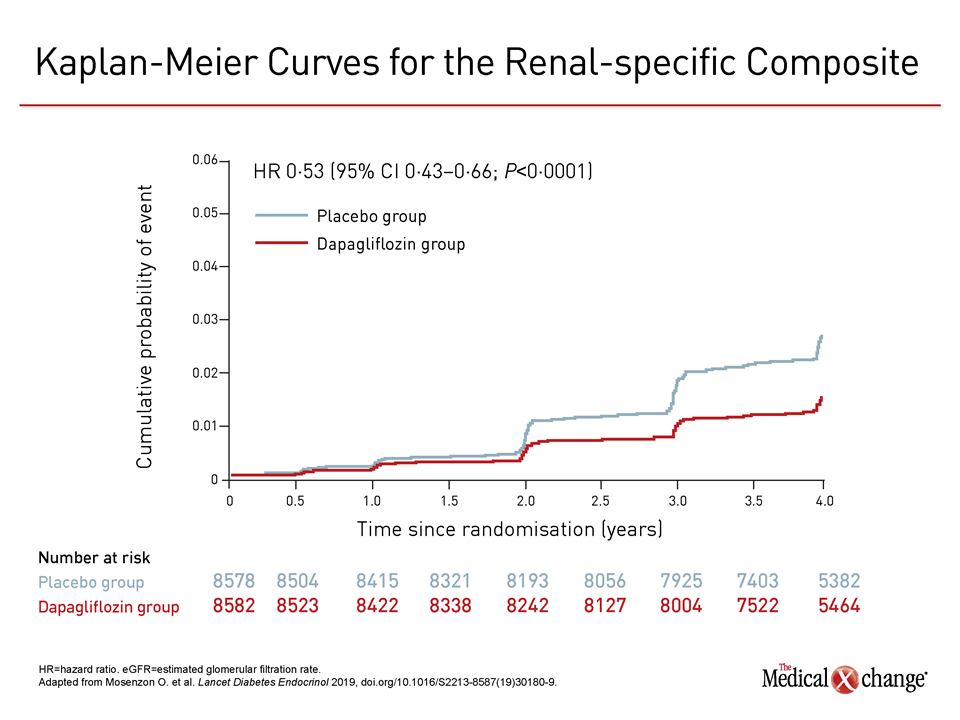
2 Studies show that lifestyle modification can lead to prevention or remission of diabetes, mainly through weight loss. 1 This high disease prevalence parallels that of obesity. However, the researchers stress that this can only be considered as hypothesis-generating, because of the nonsignificant reduction in the MACE endpoint.Prediabetes and type 2 diabetes mellitus are highly prevalent in the United States, each affecting approximately 38% and 12% of adults, respectively. The secondary renal composite endpoint in DECLARE-TIMI 58 (≥40% eGFR reduction to <60 mL/min per 1.73 m 2, end-stage renal disease, or renal/CV death) was significantly reduced by dapagliflozin treatment, at 4.3%, compared with 5.6% with placebo. Watch John Wilding discuss DECLARE-TIMI 58
TIMI TRIALS TRIAL
And the CANVAS trial showed a significant 14% MACE reduction associated with canagliflozin treatment among its 10,142 participants, two-thirds of whom had established CVD. Of note, the difference in MACE rates among patients with established CVD in DECLARE is similar to the significant difference of 10.5% versus 12.1% seen with and without empagliflozin treatment for the 7020 patients in EMPA-REG OUTCOMES, all of whom had established CVD. This difference was not statistically significant, with a hazard ratio of 0.90 and a 95% confidence interval of 0.79 to 1.02, and the test for interaction was also nonsignificant, meaning there was no statistical evidence to support a different effect of treatment in patients with and without established CVD. MACE tended to be reduced with dapagliflozin treatment in the 6974 patients with pre-existing CVD, at 13.9% compared with 15.3% among patients taking placebo. The researchers note that, overall, this fits with previous findings that SGLT2 inhibitors are more effective against HF and renal outcomes than against atherosclerotic CVD, and that for the latter they are likely beneficial only for patients with established CVD.

In this subgroup the MACE rates with dapagliflozin and placebo treatment were 5.3% and 5.2%, respectively. This was particularly the case for the 10,186 patients who did not have pre-existing CV disease (CVD) but did have multiple risk factors, with hypertension, dyslipidemia, or current smoking in addition to being aged at least 55 or 60 years for men and women, respectively.
However, in the trial population overall, dapagliflozin treatment did not significantly reduce the risk for the other primary endpoint of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE CV death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke) during a median 4.2 years of follow-up. Lead study author Stephen Wiviott (Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, USA) and colleagues report that this effect was seen both for patients with established CVD (7.8 vs 9.3%) and for those without (2.8 vs 3.4%).Īnd they stress: “The majority of patients did not have a history of heart failure, so the prevention of new clinical heart failure is notable.” The rate of the co-primary endpoint of CV death and hospitalization for HF was significantly reduced by treatment with dapagliflozin 10 mg/day, at 4.9% versus 5.8% for placebo, driven entirely by a 27% reduction in HF hospitalization (rates of 2.5 vs 3.3%). Patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) below 60 mL/min per 1.73 m 2 were excluded.Įxpert video commentary: Miles Fisher discusses the DECLARE findings The study participants were aged 64 years, on average, with a median diabetes duration of 10 to 11 years, and an average glycated hemoglobin level of 8.3% (67 mmol/mol).
TIMI TRIALS FULL
The investigators presented the full results today at the American Heart Association Scientific Sessions in Chicago, Illinois, with simultaneous publication in The New England Journal of Medicine.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
